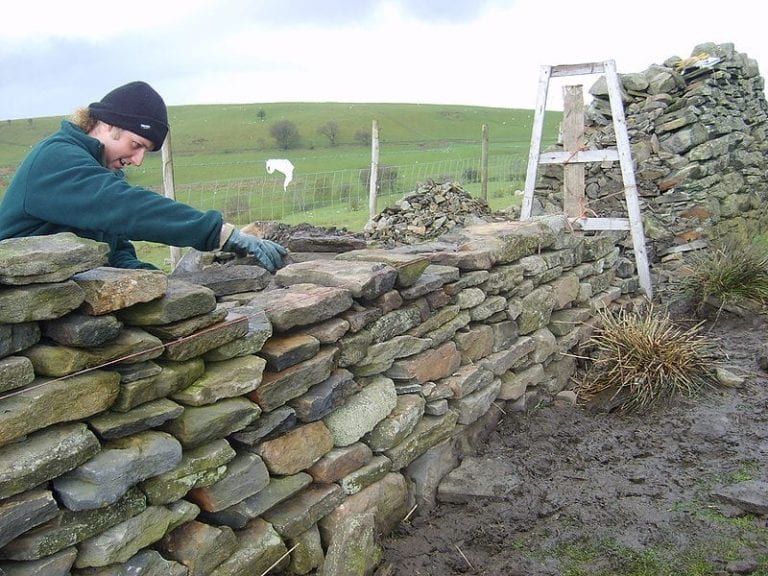
The recognition
The one ratified in Port Louis (Mauritius) and unanimously by the 24 member states is an entry into the intangible cultural heritage of humanity that is not only in Italy, where dry stone walls are present from the north (Karst, Soave, Cinque Terre, for example) to the extreme south (Pantelleria, Salento, Campania), and not just for viticulture. The practice, in fact, as enshrined in the recognition of the United Nations organism, also belongs to Cyprus, Croatia, France, Greece, Slovenia, Spain and Switzerland, in different agricultural sectors.
Italian UNESCO
Out of the nine Italian elements recognized by UNESCO as intangible heritage of humanity, four belong to rural and agricultural heritage: in 2010, the Mediterranean Diet was registered as the first cultural element in the food-related world on the UNESCO list; in 2014, the recognition of the cultivation of the alberello vine of Pantelleria, the first cultural element in the world of agricultural character in Unesco; in 2017, it was the turn of the art of Neapolitan pizza chef. The candidacy of the rural practice of dry stone walls was carried out by the Ministry of Agricultural, Food and Forestry Policies, in synergy with the Maeci body and with the Unesco National Commission.
Rural culture
"Once again," the minister for Agricultural policies, Gian Marco Centinaio commented "the values of agriculture are recognized as an integral part of the cultural heritage of peoples. Our agri-food products, our landscapes, our traditions and our know-how are characteristic elements of our history and our culture”. The dry stone wall technique gives rise to constructions with stones laid one on top of the other without the use of other materials, with the exception of the soil.
Dry stones
The stability of these structures is ensured by the positioning of the stones. All over Europe there are numerous landscapes characterized by these constructions, which have influenced farming and breeding methods. Moreover, as Coldiretti recalls, they play a fundamental role in the prevention of landslides, floods and avalanches and in the fight against erosion and desertification, increasing biodiversity and creating adequate microclimatic conditions for agriculture.

 In the United States, it’s Prosecco mania – despite Trump’s tariffs. And the credit goes to women
In the United States, it’s Prosecco mania – despite Trump’s tariffs. And the credit goes to women In Romagna, there's an osteria opened in an old rectory that has breathed life back into a depopulated village
In Romagna, there's an osteria opened in an old rectory that has breathed life back into a depopulated village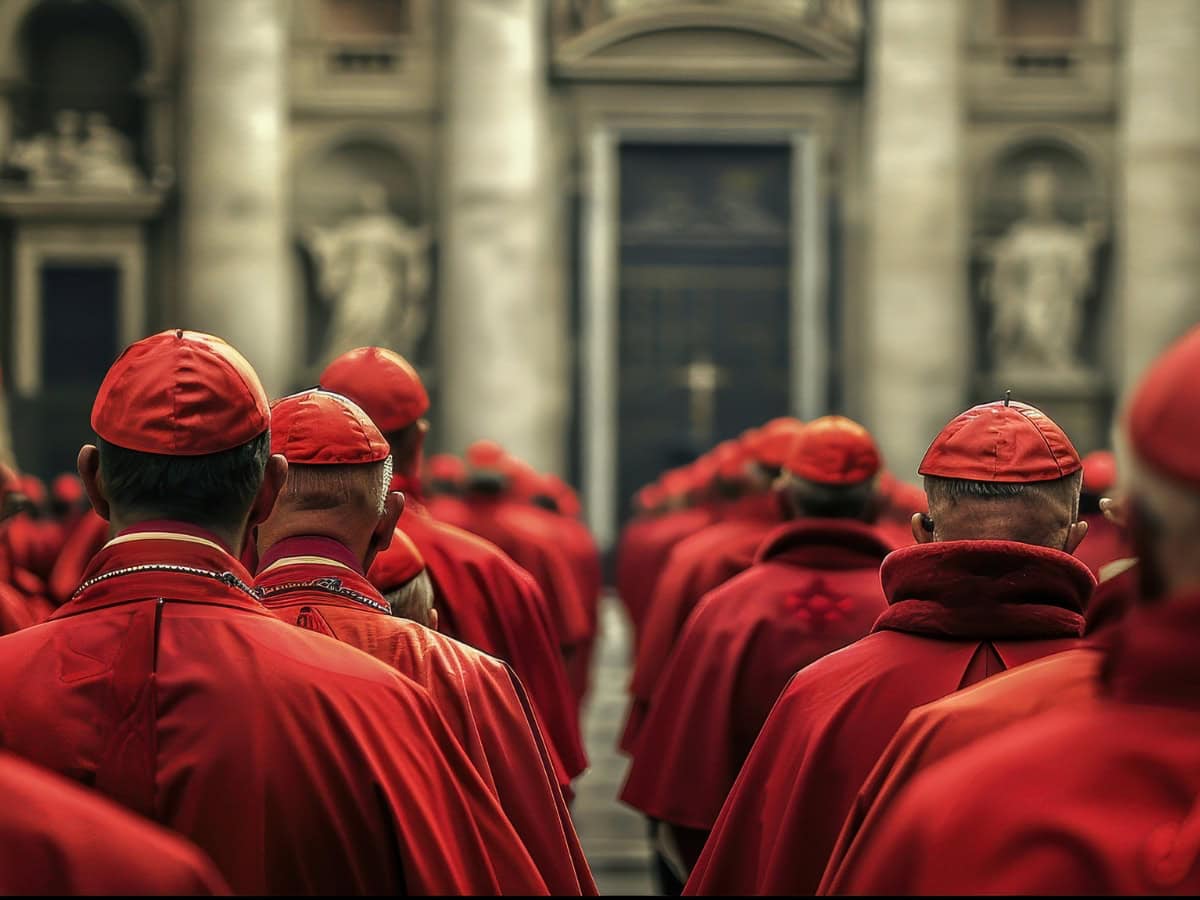 Dining with the Cardinals: here’s what they eat during the Conclave
Dining with the Cardinals: here’s what they eat during the Conclave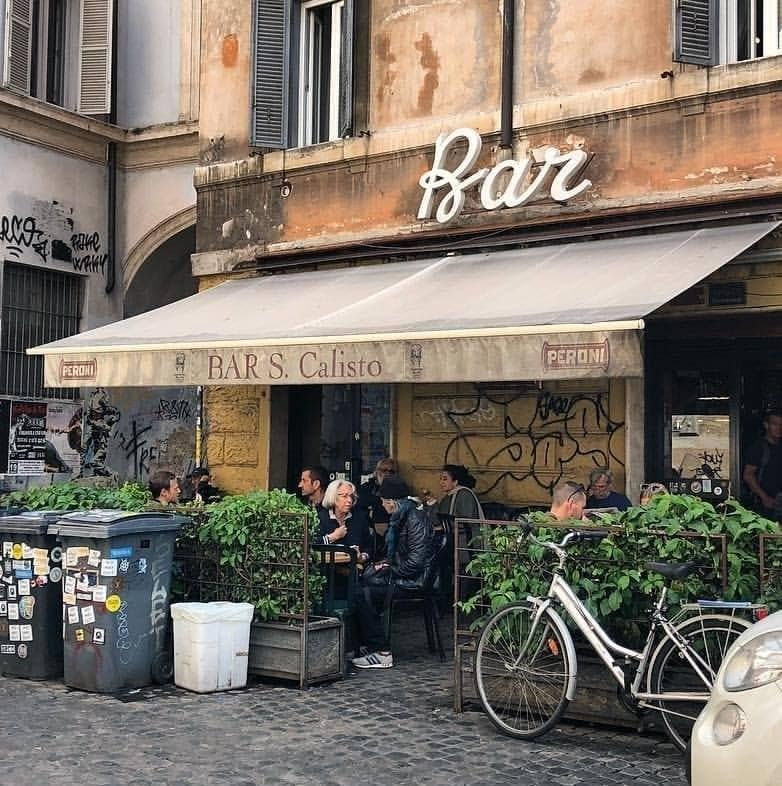 Why tourists love Bar San Calisto in Trastevere
Why tourists love Bar San Calisto in Trastevere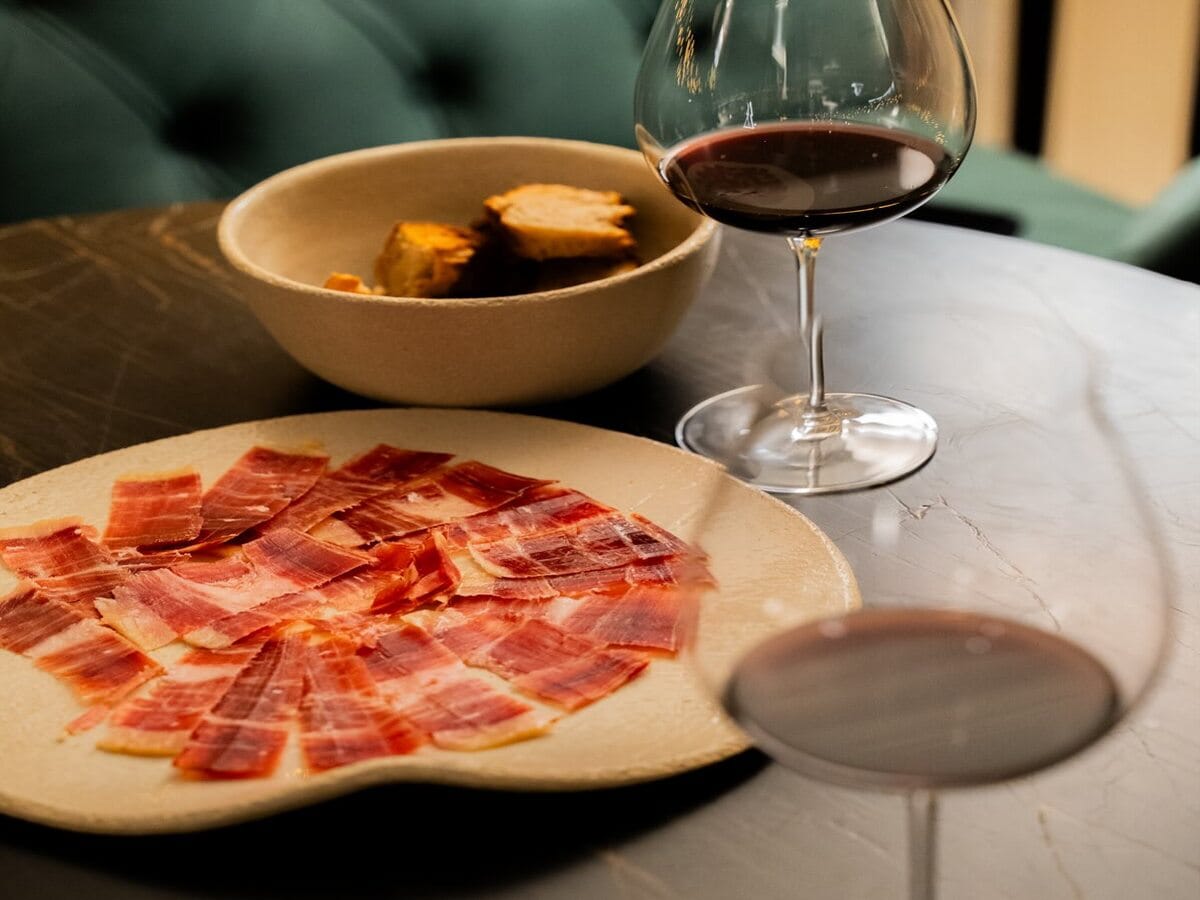 Where to drink in Milan: the best wine bars with kitchen selected by Gambero Rosso
Where to drink in Milan: the best wine bars with kitchen selected by Gambero Rosso